Increasingly, machine translation (MT) is being used by companies large and small to translate text quickly and cost-effectively. Particularly on enterprise-scale projects, it plays a crucial role in delivering impactful localized experiences to global audiences in a timely fashion.
In decades past, it was viewed by many as unsuitable for translating important or high-visibility content, and for translating content at scale due to the quality of the translations. But fast forward through recent years up to today, and the prevailing opinion has changed dramatically.
There have been numerous advancements in machine translation that have improved translation results dramatically, and we’ve also seen considerable expansion in terms of MT’s use cases. In particular, neural machine translation (NMT) is better than ever as an option for businesses looking for a balance between quality, cost, and speed. If you’re not yet leveraging NMT in your workflows, now’s the time to consider it.
How does neural machine translation work?
Neural machine translation uses neural networks to replicate the human translation process at an accelerated pace. These networks are made up of layers of connected nodes that transmit signals, much like the networks of neurons in the human brain do. Put simply, one layer encodes the source text and another decodes it into the target language, using knowledge acquired from training on massive datasets.
Then there’s the third component of NMT, which “connects the dots” between the encoder and decoder. It’s called the attention mechanism and helps the decoder accurately weigh how much each word in the input sentence should impact the translation of the current output word. In other words, it’s what helps machine translation engines understand the context of source text and deliver accurate translations in response.
The many advantages of leveraging neural machine translation
What can you expect to gain by incorporating neural machine translation into your translation mix?
- Faster time to publish. Unlike human translators, neural machine translation engines can translate billions of words instantly.
- Cost savings. The cost of machine translation typically ranges from as little as $0.005 to $0.0012 per word with Smartling, much less than human translation costs. The money you save from MT can then be invested into human translation and quality assurance for high-touch translations (or other business initiatives that require specialized translation).
- Improved scalability. Thanks to NMT’s speed and cost-effectiveness, you can scale your translation efforts more easily. In other words, you can translate large amounts of text without dramatically increasing costs and get to market faster.
- Linguistic consistency. Neural machine translation is able to ensure consistency with company terminology via your style guides, glossaries, and translation memories.
- Improved quality (as a result of customizability). You can achieve even higher quality and consistency with NMT if you train a custom engine on company and domain-specific terminology. The cherry on top is progressive improvement. Neural machine translation systems effectively "learn" over time. As they process more data, the translations they produce continuously improve. This amplifies all of the benefits above.
Addressing challenges and limitations of NMT
Awareness is the first step in managing the limits and challenges of neural machine translation while ensuring translation quality. So, what do you need to know?
- NMT is better at understanding source text than statistical machine translation. (The latter basically used statistical probability rather than context to predict the most likely translation of words.) However, neural machine translation can still get things wrong sometimes even with its ability to consider context.
- Neural machine translation sometimes lacks cultural context and may be unaware of certain sensitivities. In other words, NMT systems aren’t currently equipped to make judgment calls on what may need to be excluded from a translation or adapted so as to be more well-received by your target audience.
- Humor, slang, and figures of speech may sometimes be mistranslated. This may be because of misjudgment of context or because there’s no direct translation of a word or phrase in your target language, meaning the word-for-word translation will not make sense.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) in general is trained on massive datasets that often contain human biases related to gender, occupation, and so on. As a result, AI outputs—including machine translation results—can retain those biases.
The main way to address these problems is to have qualified humans in the loop for quality assurance purposes. NMT engines have advanced to the degree that they can be useful for and deliver good quality across most content. But, in many cases, it’s wise to employ human review and machine translation post-editing (MTPE) to catch and correct any errors or inconsistencies before translated content is made available to your audience.
Additionally, it’s valuable to know when to opt for human translation instead of MT. You might choose human translation for high-touch marketing campaigns or when domain expertise (specialized translation services) is needed.
It’s also smart to opt for solutions that specifically address nuanced challenges like bias. For instance, Smartling’s revolutionary, patent-pending AI technology analyzes context to produce gender-accurate translations thereby preventing confusion or offense.
Best practices for incorporating NMT into your workflows
Despite its current limitations, incorporating neural machine translation into your translation workflow can significantly improve its efficiency and lower your translation costs. Here are some additional tips on how to get the best out of NMT:
- Choose your machine translation engine thoughtfully. Not every engine works optimally for every use case, need, or budget. So, consider factors such as pricing, supported language pairs, customization options, and integration capabilities when evaluating different vendors.
- Use an engine optimized for your domain. Especially if you’re in a technical or scientific industry with a lot of important terminology, you’ll be better off using an engine that’s optimized for your domain. One may already exist, or you may choose to train one, which would give the added benefit of being able to update training data to improve translation quality over time.
- Consider pre-editing. Clean, well-structured text with little to no ambiguity will yield better translation results. You can use a tool like our GPT-enabled translation portal Smartling Translate to clean text up before translating it with MT.
- Monitor and evaluate translation quality: Establish a feedback loop to monitor the quality of your NMT output and make necessary adjustments. This will involve gathering feedback from translators, reviewers, and end-users to identify areas for improvement. But, as Mei Zheng, our Senior Data Scientist pointed out in our Reality Series episode on machine translation quality estimation, it also encompasses mapping automated quality estimates to human estimates.
Mei said, “If you have the resources to do automatic scoring on all of your content, definitely do that. Then, sample some of those strings for evaluation by humans. This way, you get a baseline of what that automatic score corresponds to when a linguist sees it.”
This baseline will allow you to estimate at a glance how much attention a translated text needs in terms of post-editing if it needs any at all. The end result is not only increased efficiency but also improved quality.
What are some of the top NMT engines?
There are many neural machine translation engines available, as well as large language models like GPT that rely on NMT. Here are three of the most popular and reliable options—all of which integrate with Smartling.
Google Cloud Translation API
Google Translate is, of course, a popular translation tool but it’s best for shorter snippets of text or sporadic usage. If you’re an enterprise localization manager, for example, and need to translate content at scale, you’ll need Google Cloud Translation API.
Top features:
- Model training and management: Train a custom machine translation model to get more precise translations tailored to your domain and context.
- Batch translation: Translate content in bulk to speed up your workflows and decrease time to publish.
- Application programming interfaces (APIs): Choose between the REST and gRPC APIs to integrate Google’s translation results with other software.
Pros:
- There’s no limit on the amount of characters you can translate per day (either with the Basic or Advanced plans).
- The translations improve over time through input from native speakers.
- Google Cloud Translation has an offline mode, so you can keep translating without an internet connection.
Cons:
- Google Cloud Translation API plans offer less flexibility than competitors. For instance, the basic plan doesn't support glossaries and only handles two content types.
- According to one user, Google Cloud Translation API can be expensive if you have massive amounts of text to translate. (Source: G2)
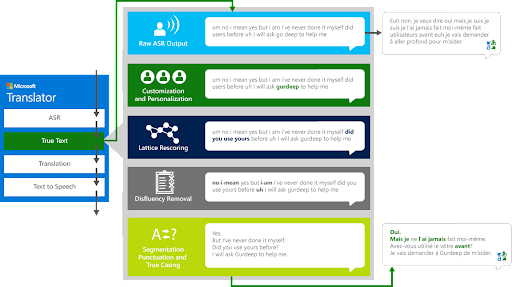
Microsoft Translator
Next is Microsoft Translator—a cloud-based machine translation service that supports translation in over 100 different languages. It can be integrated into apps, websites, and other products via its REST API or SDKs.
Top features:
- Custom Translator: Train industry or domain-specific models for more accurate, high-quality translations tailored to your content.
- Lookup: Find alternate translations and understand word context using the Dictionary Lookup and Examples tools.
- Batch processing: Translate many texts or documents in one API request without character limits.
Pros:
- Microsoft Translator is suitable for many use cases, including customer support, live and remote communication, ecommerce, business intelligence, internal communications, and more.
- If you’re an avid Microsoft user, you’ll love Translator’s integrations with other Microsoft products, including Office, SharePoint, and Bing.
- No texts or data are stored in Microsoft’s data centers, and Translator complies with security and privacy regulations like HIPAA.
Cons:
- Translation accuracy and fluency are not as good as other NMT engines like DeepL for some language pairs.
- Linguistic nuances like slang or informal speech may not always be translated correctly.
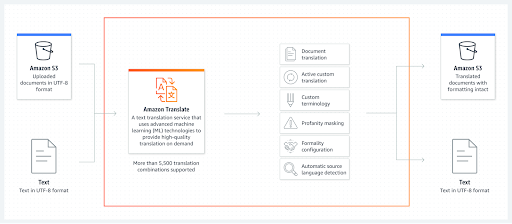
Amazon Translate
This neural machine translation service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) uses deep learning to deliver fast, high-quality, and affordable language translation. Like the alternative covered above, it’s designed to deliver accurate and natural-sounding translations for a wide range of use cases.
Top features:
- Automatic source language detection: Amazon Translate can identify the language without language codes.
- Named entity translation customization: Specify how the model should translate words or terms specific to your industry, domain, or organization.
- Active Custom Translation: Customize translations without building models from scratch.
Pros:
- Pay-per-use pricing provides a cost-effective option for growing translation needs.
- You can translate Word docs, spreadsheets, and more in bulk via the TextTranslation API.
Amazon Translate supports 5,550 language combinations across 75 languages.
Cons:
- You’ll likely need a developer to handle the coding for the Amazon Translate integration.
- Some users have experienced issues with accuracy, mechanics, and untranslated detected words/phrases.
One centralized hub for all the best MT engines
As you saw above, every machine translation engine has its strengths and weaknesses. Even beyond the pros and cons we talked about, some engines are best for certain domains or industries. Others are better for specific language pairs or content types. That said, it’s in your best interest not to be limited to a single engine, and the proof is in the pudding.
Our customers routinely receive up to 350% higher quality translations thanks to Smartling Autoselect, which automatically chooses the best MT engine for their content and locale pair. This multi-engine approach ensures that you’re always getting the highest-quality machine translations possible. (Smartling Autoselect is available in our Neural Machine Translation Hub, where you can integrate various engines, including DeepL, Microsoft Translator, and Google Cloud Translation.)
For a closer look at our translation management system, which includes the Neural Machine Translation Hub, watch our five-minute demo. We’ll be happy to get you set up afterward if you decide you’d like to see for yourself how it works.