The mobile ecosystem is healthier than ever. In 2021, 230 billion mobile app downloads were registered, resulting in a $170 billion consumer spend. Moreover, with consumers spending 3.8 trillion hours on their mobiles, it's not surprising that companies are investing more money into building mobile applications.
However, a larger investment doesn't always equate to a more extensive user base. In today's global and multicultural world, it's becoming increasingly crucial to fine-tune one's app strategy for different markets.
This is where localization comes into the picture.
Mobile app localization refers to translating an app's text and non-text elements into a different language. It's important to note that it doesn't only focus on translating the text but also tailoring the entire user experience (UX) for the consumer based on their cultural preferences.
This article will discuss the benefits of localizing your app, types of mobile app localization, how you can create a robust localization strategy, and the roadblocks you can expect.
The importance of mobile app localization
The goal of mobile app localization is to create an experience that feels natural to users in their native language. In turn, it increases their affinity towards the app, which leads to more downloads and revenue for the company.
A common misconception is that you can use “localization” and “internationalization” synonymously. That's not true.
Localization focuses on adapting existing app content to new languages or geography. This process involves adapting every single piece of content for the target market’s language and cultural nuances. For example, the website, app, images, video, internal marketing collaterals, currencies, etc. needs to be localized completely. It can be done at a later stage and will require significant changes at the code level to support multiple languages.
On the other hand, internationalization focuses on offering a global experience from the development stage. You build your application or product in a way that it supports multiple languages and writing conventions at a later stage. Ideally, developers build the entire architecture to accommodate these changes, ensuring a smoother transition later.
A CSA Research Report found that 35% of respondents indicated that they use documentation in a foreign language daily. If you don't localize your app, you're missing out on a huge user base for an avoidable reason.
There are several reasons why you should localize your application. Here’s a list of the potential benefits:
1. Tap into high-growth and emerging markets
App localization helps businesses tap into emerging markets by making their apps available in more than one language.
For example, a business might want to develop an app for the Chinese market because they know that there are many potential customers in China. They could translate their app into Chinese and submit it to the Apple (iOS app) or Google Play Stores (Android app) to reach these customers.
Localization also helps companies build customer trust and gain a competitive advantage over other brands that haven't localized their apps. They can identify these markets by looking at recent reports or speaking to new customers from such markets.
The number of app downloads by country (2019 to 2021)
2. Improve user experience for a global audience
User experience is a key factor for global app engagement and usability. If your mobile app doesn’t offer a consistent user experience, it’ll impact your bottom line.
Even though users download these apps, once they find out that it has a terrible user experience or doesn't cater to their linguistic needs, they tend to uninstall them. A properly localized app can retain users and increase app engagement.
Your app must be translated into different languages and adjusted for cultural differences. For example, you can't translate your app into German and expect it to work equally well in Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, even though there are German-speakers in each country.
3. Improve searchability in different search engines
Localization can improve your app's chances of discovery by potential users. Your app will be visible under location filters when people search for products like yours on app marketplaces.
When people see a localized version of your app in their language or country, they’re more likely to download it than if they saw the default English version available worldwide.
Plus, if your app has a good rating, it'll help you rank higher in app stores. One of the ways you can achieve a high rating is by offering a localized version.
4. Increase app downloads in different target markets
App localization isn't just about reaching new markets—it's also about improving customer satisfaction. When you offer a localized version of your app, it increases accessibility.
When users see that you offer a localized version of your mobile app, it's highly likely they will also download the app. A simple way to identify such markets is to observe if you've recently acquired new users from other geographical regions.
Increase revenue and positively impacts your bottom line
A recent study found that 66% of B2B buyers are willing to invest more in an app if it offers a local language experience. As for B2C buyers, that number comes down to 34%.
In either case, it goes to show that not only are buyers willing to purchase the product, but they'll also invest a higher amount just to receive that experience. It results in increased revenue and satisfied customers.
If you forego globalization, eventually you’ll lag behind your competitors. As more competitors invest in such technologies and consumers demand them, offering this option differentiates you from the competition.
Types of mobile app localization
As application localization is a comprehensive and time-consuming process, it's always best to test a small prototype before delving into the project. Based on the project's scope, there are two ways to localize your app.
Minimum viable localization (MVL)
The first step towards app localization is deciding how much effort and resources you want to invest in this process.
The most basic form of app localization is minimum viable localization (MVL). It aims to localize only the app's key aspects like keywords, descriptions, pricing, payment options, metadata, etc. It's the bare minimum you need to test the waters and analyze whether it works.
For example, an app developer translated the keywords of his gaming application "Abe the Dragon" and observed an increase of 767% in global downloads. His MVL approach indicated the potential of localizing for these regions.
Full app localization
If you’ve tested the waters successfully, conducting a full app localization is the next step. It goes beyond store listing descriptions. Instead, you must focus on translating the elements, fine-tuning the user experience, and marketing the product in those regions.
Corey Haines, Co-founder of Swipewell, adds, "Everything from your website, blog, app, and terms of service have to be translated. And that's just table stakes. Then, you have to advertise and build an online presence in each locale. The best way to do this is to hire a marketer for each region you want to expand to who can speak the local language(s) and then give them a budget to spin up marketing programs for that market."
For example, Lyft localized its website and mobile app in eight different languages. These efforts resulted in a 51% increase in page views and a 29% increase in on-page time amongst non-native English speakers.
How to create an app localization strategy
Here are eight steps you can use to create a robust app localization strategy:
1. Speak to your customers or review in-app feedback
Before finalizing the semantics of your localization project, it’s crucial to talk to existing customers first. They’ve used your application and have enough experience to pinpoint real localization gaps.
You can achieve this by diving into your app’s analytics dashboard. You need to look for three types of customers from:
- Your target market but choose alternative languages
- A non-target market but continue to use the app
- A non-target market but uninstalled it upon download
Each of these customers can give you insights into what's working for them and what isn't. For example, customers from a different target market who continue using this app might have a lot to add about their preferences. They can provide information on the in-app experience in their country, what features need to be localized, etc.
Moreover, you can dig into customer requests to see if certain customers are looking for a specific feature. In some cases, they might have trouble translating it into their language. There are plenty of sources to dig into—analyze them with a fine-tooth comb.
2. Determine which markets you need to target
Once you have the customer data, determine which markets you need to target. Although customer data is not the only resource you can use, it gives you direction on which markets to prioritize.
You can also look at recent reports in the market and identify which languages are prioritized in app marketplaces. This approach will give you an idea of markets now or at a later time point.
Another approach you can take is to see which markets your competitors are catering to. For example, if your competitors focus on emerging markets like China, Brazil, and India and you're only focusing on English-speaking countries, there's an opportunity.
Most common languages used on the internet as of January 2020
3. Research your target market
Once you've identified potential languages you can focus on for your localization project, you must conduct thorough research.
Through research, you can discover the following:
- Countries that use a certain language
- Demographics of a specific country
- Number of dialects present
- Potential user base for your app
- Cultural nuances to incorporate
- Regional graphics and color preferences
- Popular types of content formats
- Socio-cultural influences of the user base
- Popular search phrases in specific app marketplaces
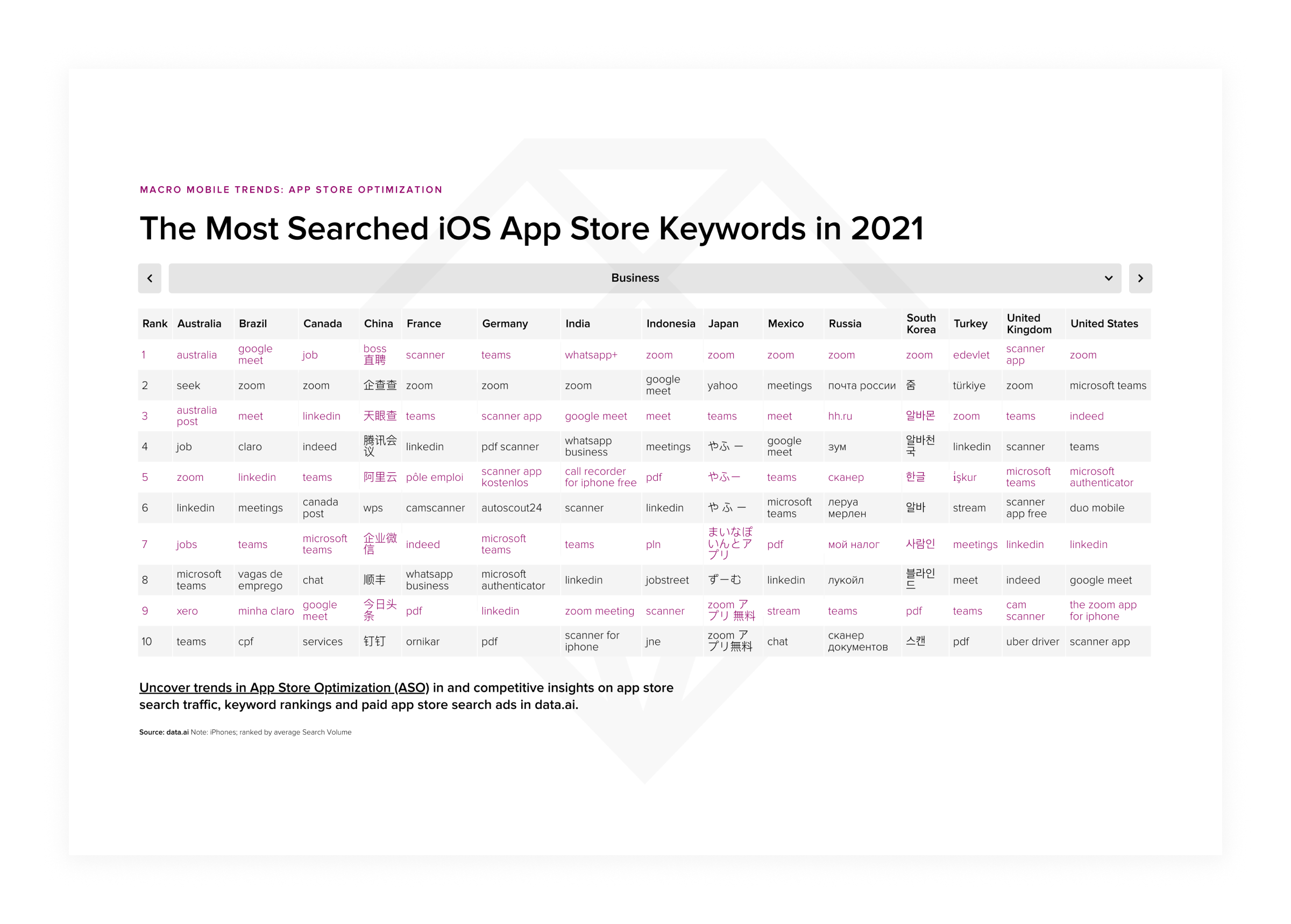 The most searched iOS app store keywords (2021)
The most searched iOS app store keywords (2021)
4. Decide which languages or regions take priority
Now, you can devise a clear strategy on which languages or regions should take priority. There’s no need to rush the application localization process—especially if you’re doing it for the first time.
The entire localization process can be time-consuming, so choosing a single language or region makes it easier. You can decide this based on your market research, competitor analysis, and user feedback.
Essentially, you need to determine which markets are worth the investment right now. If you observe a slight increase in users from a non-target market, determine if the localization and marketing investment will provide an acceptable ROI.
5. Finalize the localization project’s budget
Most businesses might not have the time or money to translate their apps into multiple languages fully, hire translators, and develop localized marketing materials.
The cost of app localization varies based on the number of supported languages, the number of countries supported, and any additional functionality (like voiceover support, video translation, etc.) included with your project.
Plus, it depends on your goal. For example, are you working on your MVL or implementing a go-to-market strategy? Based on this, your internal team or translation service provider will give you an estimate. Then, you can consider the potential ROI of the project before making a decision.
6. Determine KPIs to measure ROI
Without clear key performance indicators (KPIs), it’s challenging to measure the true ROI of your localization project. Here's a simple formula:
ROI = (Current added value of localization - Cost of localization) ÷ Cost of localization
Here are a few other metrics you can use to measure translation ROI:
- App visibility like page views, likes, and shares
- Campaign analytics from different markets
- Increase or decrease in app downloads
- Positive or negative reviews (in-app or on review sites)
- In-app engagement rates
- Paid conversion rates
- Increase in market share
For example, Lucidchart realized a 200% YoY growth in the Latin American market. This resulted in 125,000 product users in just 4 months.
For paid conversion, measure the impact of your app store optimization (ASO) efforts by comparing it with benchmark reports like AppFollow’s report.
AppFollow’s Conversion Rate Benchmark Report
7. Conduct research on localization services
There's no use in cutting corners here—any user who tries your app in their native language will immediately notice a bad translation. For this reason, hiring professional translators or translation management services like Smartling is essential to localize your app successfully.
Keith Brooks, CEO of B2B Whisperer, adds, "This is probably obvious, but you really need a native language speaker because, without them, you will not get the right translations or idioms. Second is a complete list of everything you need to be translated so there is a guide/dictionary and you don't repeat efforts."
Plus, experienced translators can differentiate between cultural nuances and account for context, too (something that software programs can't always achieve).
8. Finalize the mobile app localization workflow
You can break down the mobile app localization workflow into three main phases:
- Planning and analysis: This stage includes determining the project timelines (including check-in, deployment, and testing).
- Translating text and assets: This stage includes translating all text within the app, including the app title, descriptions, instructions, tutorials, and any screenshots or graphics used throughout the app.
- Testing and publishing updates: Once all translations have been completed and tested by native speakers from each country, it's time to publish them on the platform store(s) where your app is available (like the Google Play Store and Apple App Store).
Localization testing or quality assurance (QA) is often overlooked. Keith adds that this is “usually due to resource limitations. The user interface may look right, but if you run a process, do you get the proper answer in the right language? If it is a bi-directional language like Arabic or Hebrew, do you get the answers written correctly, right to left?”
So, implement a solid QA process before you get started.
Common challenges of mobile app localization
Even though localization is needed, you might encounter several bottlenecks no matter how much planning you do. To help you prepare, we've listed out a few roadblocks below:
1. Increases time to market and associated costs
It's essential to take the time to localize your app before you launch it. But doing so takes time and can increase costs. By delaying app release, developers are prevented from working on new functionality because they’re waiting for translation.
Moreover, if you don't have a solid localization workflow beforehand, it could result in delayed feature launches. This happens because developers must wait for the feature to be localized before launching it every time. It’s best to tighten these processes and conduct them simultaneously to reduce costs and time to market.
2. Not knowing how much to localize
In some countries, localization needs may not be as intensive because of potential similarities.
For example, if you're translating your mobile app from English spoken in the United States to English spoken in the United Kingdom, the literal translation will remain the same. However, the cultural nuances and technicalities will change.
Vanhishikha Bhargava, B2B SaaS Content Marketer, says, "This is often due to the dynamic markets where local and global languages like English get used—whether for work or personal communication. This also results in the lack of consistency in the localization of the app experience; which is often broken. And we've seen many apps that have an in-app dashboard that is localized in terms of the language, but when it comes to numbers, they use global standards."
3. Incorporating the right cultural context
Google Translate can't capture the nuances of different languages. For this reason, it's essential to have a healthy balance between machine and human translation.
For example, while the thumbs-up emoji might mean “good job” or a simple A-OK to you, in countries like Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Nigeria, it has an offensive meaning.
Keep these cultural nuances in mind. Failure to do so can result in a flat go-to-market campaign and loss of investment.
4. Making space for other languages
The impact of lettering is often overlooked. While you might think that all you have to do is translate and upload the translated asset, you’re missing a huge aspect—the expansion or contraction of letters. If the text expands it’ll occupy more space on your app, leading to a massive impact on UX.
Think about how text expands or contracts when translated. Here are a few predicted numbers:
- English to German: +35%
- English to Arabic: +25%
- English to Korean: -15%
- English to French/Spanish: +20%
Here's an example of how an English-to-German translation impacts the UX of the TED app:
TED’s mobile app: UX differences between English and German copy
5. Disregarding right-to-left lettering languages
Too often, companies get caught up in localizing for PFIGS (Portuguese, French, Italian, German, Spanish) languages but forget the rest. As these are left-to-right lettering languages, it's easier to optimize for them.
However, it's another ballgame to achieve the same for right-to-left lettering languages like Arabic, Hebrew, Persian, etc.
David Bitton, Co-founder and Chief Marketing Officer of DoorLoop, says, "These aspects necessitate rearranging numerous UX components, which you must remember to do before your program looks disconnected and degrades the user experience."
The UX expectations of these users are entirely different from those who delve into left-to-right lettering languages.
“For instance, individuals accustomed to writing from left to right will anticipate seeing the ‘Next’ button on the right. The opposite is true for users accustomed to writing from right to left. Making a mistake here can make it difficult for local users to become accustomed to using your software and will result in decreased user numbers,” notes David.
6. Forgetting the bigger picture
When the project is ongoing, it's easy to get caught up in the minute details. Maybe you're more focused on maintaining brand personality or stylistic tone, but the cultural nuance doesn't allow it. You might be wondering about the best way to work around it.
Ideally, focusing on the user’s needs is paramount. Jon Macdonald, Founder and CEO of The Good, says, "We often find that clients want to agonize over the finer and more technical points—how to deal with translations, whether or not to place a country flag on the site, whether to use a drop-down box or tabs for country selection, and such before making larger choices on understanding what the customer wants."
Think about what your customers want and adapt your app to meet their needs. Doing so will only increase their affinity towards your brand and encourage paid conversions down the line.
Final thoughts
Global opportunities are growing, but challenges with language and cultural barriers remain. Localizing your app for different target markets is vital—yet tricky.
Establishing the right budget, partner relationships, and translation platforms to localize your app accurately and cost-effectively takes time. However, it’s not impossible.
You can always test a smaller market first, then graduate to a full-fledged localization strategy. Plus, the research process can give you valuable insight into the specifics of your final localization strategy. You can either do this yourself or hire experienced localization professionals to achieve this successfully.
If you're looking for a service to manage your end-to-end localization needs or translation management software to scale your localization efforts, book a meeting with Smartling today.